Hinton is used for plotting the real and imaginary parts of the state matrix on two-dimensional plots. Qiskit provides inbuilt function to create Hinton visualizations. In this chapter of the Qiskit Tutorial, you will learn about how to create Hinton visualizations by making use of the visualization module of qiskit.
Hinton plots are similar to Cityscape plots- there are two plots, one each for real and imaginary parts of the state matrix. However, since they are two-dimensional plots, instead of the height of the bar, the size of the plot is indicative of its magnitude, and the color of the plot is indicative of its direction(positive or negative). The positive values in hinton is indicated by white color, the negative values in hinton is indicated by black color, and no values or 0 is indicated by grey color.
In addition to the real and imaginary parts of the state matrix, hinton also gives information about the mixed states.
Importing Hinton Visualization Function
The plot_state_hinton() function of qiskit.visualization module creates a visualizations for the Qubit
from qiskit.visualization import plot_state_hinton()Plotting Hinton
The plot_state_hinton() method accepts data for plotting Hinton as a Statevector or a Density Matrix.
Example
In the following example, we will plot the following statevector on the hinton –
[1/sqrt(2) 0 0 1/sqrt(2)]
which represents the state: ψ = 1/sqrt(2) |00> + 1/sqrt(2) |11>
where sqrt(2) represents square root of 2.
plot_state_hinton([1/np.sqrt(2), 0, 0, 1/np.sqrt(2)])The output of this will be-
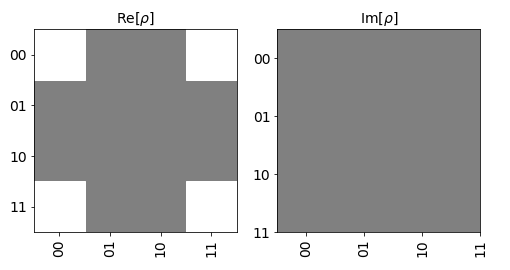
Note– Notice that there are no imaginary parts in the state matrix of the given state, hence the entire imaginary plot(on the right side) is grey. Also notice that only 4 white patches of equal size are there on the real plot(on the left side), which is indicative of the 4 real parts of the same value in state matrix at the respective positions.
Visualizing Statevector Simulator Results on Hinton
In this section, we visualize the results from the Statevector Simulator using a Hinton.
# Creating a Quantum Circuit to run on the Statevector Simulator
qc=QuantumCircuit(2)
# Applying H Gate to both Qubits
qc.h([0,1])
# Setting Backend to Statevector Simulator
backend = BasicAer.get_backend('statevector_simulator')
# Executing the Quantum Circuit
job=execute(qc, backend)
#Get results from job
result = job.result()
# Getting the count of various measurement states
state_vec = result.get_statevector()
# Plotting Hinton
plot_state_hinton(state_vec)The output of this will be-
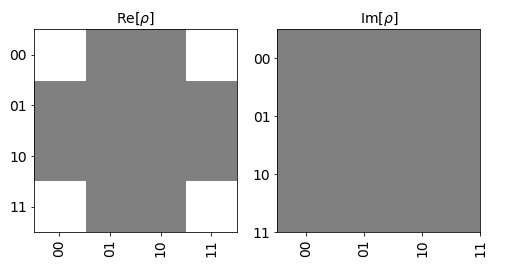
Note– The get_statevector() method returns the statevector in the form of a numpy array. Therefore, state_vec variable can be passed directly to the plot_state_hinton() function.
Parameters
The following are some of the important parameters of the plot_state_hinton() function-
| Parameter | Brief Description |
|---|---|
state | It is a Statevector or a Density Matrix that represents the state of all Qubits in the Quantum Circuit. It is usually passed as a positional parameter. |
title | It is a string that is used for the plot title. |
figsize | A Tuple that contains the size of the figure in inches. |